中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (23): 3727-3721.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.23.020
• 干细胞因子及调控因子 stem cell factors and regulatory factors • 上一篇 下一篇
碱性成纤维细胞生长因子重组腺病毒转染兔骨髓间充质干细胞的表型变化
蔡弢艺1,陈雄生2,贾连顺2,孙延卿1,林 斌1,陈长青2
- 1解放军第175医院骨科医院,福建省漳州市 363000;2解放军第二军医大学附属长征医院骨科,上海市 200003
Rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transfected with recombinant adenovirus vectors carrying basic fibroblast growth factor: variation of cell phenotypes
Cai Tao-yi1, Chen Xiong-sheng2, Jia Lian-shun2, Sun Yan-qing1, Lin Bin1, Chen Chang-qing2
- 1Orthopedics Hospital, the 175th Hospital of Chinese PLA, Zhangzhou 363000, Fujian Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Changzheng Hospital of Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China
摘要:
背景:外源性碱性成纤维细胞生长因子在韧带组织的愈合过程中发挥着重要作用,采用转基因方法将外源性基因转入细胞内能促进碱性成纤维细胞生长因子分泌。
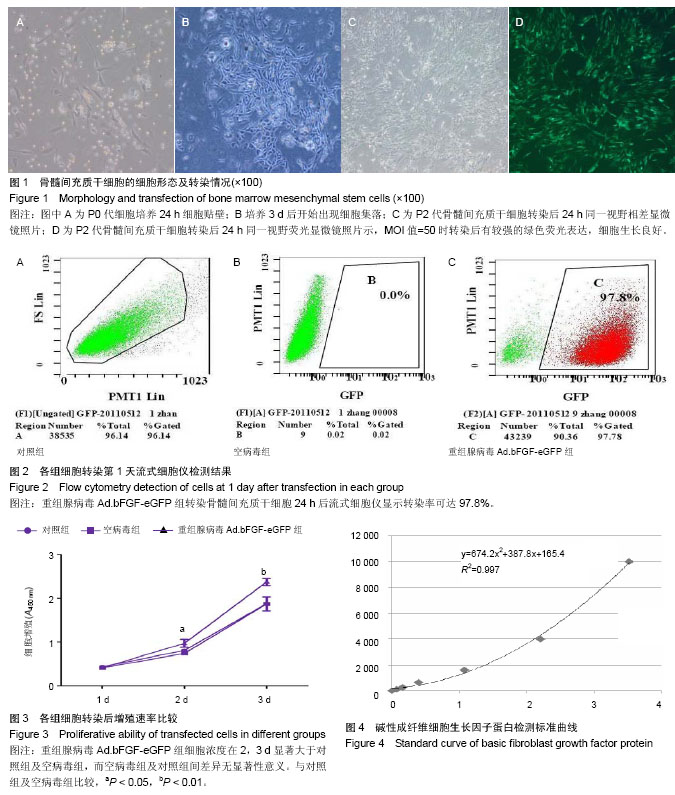
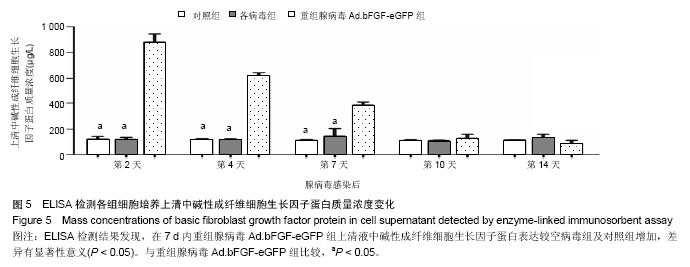
结果与结论:转染后细胞呈现均一的成纤维细胞表型;碱性成纤维细胞生长因子重组腺病毒组细胞增殖活性高于空病毒组及对照组;ELISA结果提示碱性成纤维细胞生长因子重组腺病毒组在7 d内上清液中碱性成纤维细胞生长因子蛋白质量浓度较空病毒组及对照组增加,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。提示碱性成纤维细胞生长因子重组腺病毒转染骨髓间充质干细胞可促进其向成纤维细胞分化,增加增殖活力,促进其碱性成纤维细胞生长因子蛋白的表达。
中图分类号:
.jpg)